Abstract
Class-agnostic counting (CAC) aims to estimate the number of objects in images without being restricted to predefined categories. However, while current exemplar-based CAC methods offer flexibility at inference time, they still rely heavily on labeled data for training, which limits scalability and generalization to many downstream use cases.
In this paper, we introduce CountingDINO, the first training-free exemplar-based CAC framework that exploits a fully unsupervised feature extractor. Specifically, our approach employs self-supervised vision-only backbones to extract object-aware features, and it eliminates the need for annotated data throughout the entire proposed pipeline.
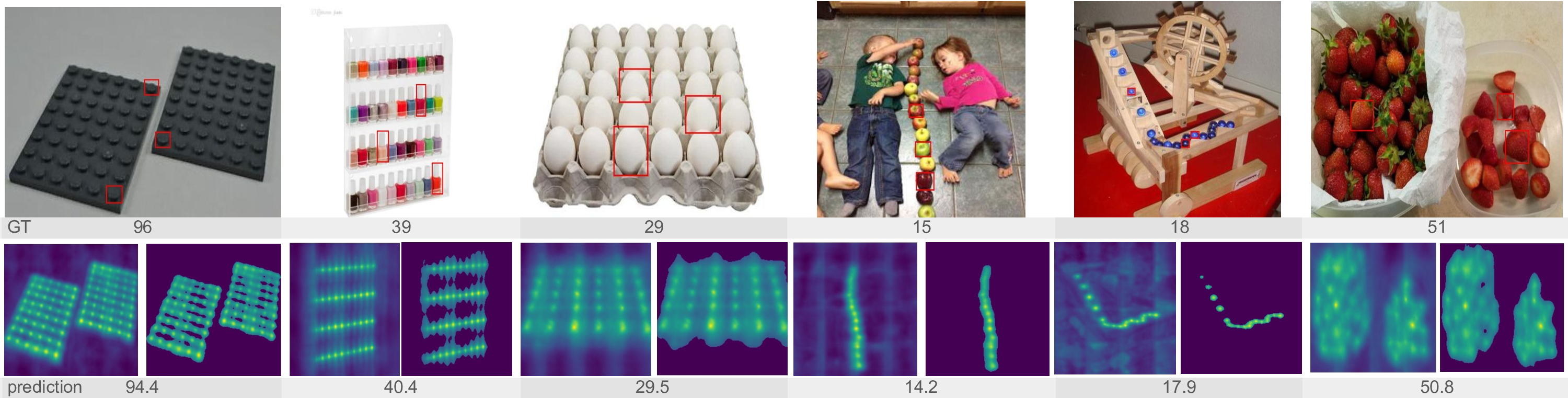
At inference time, we extract latent object prototypes via ROI-Align from DINO features and use them as convolutional kernels to generate similarity maps. These are then transformed into density maps through a simple yet effective normalization scheme.
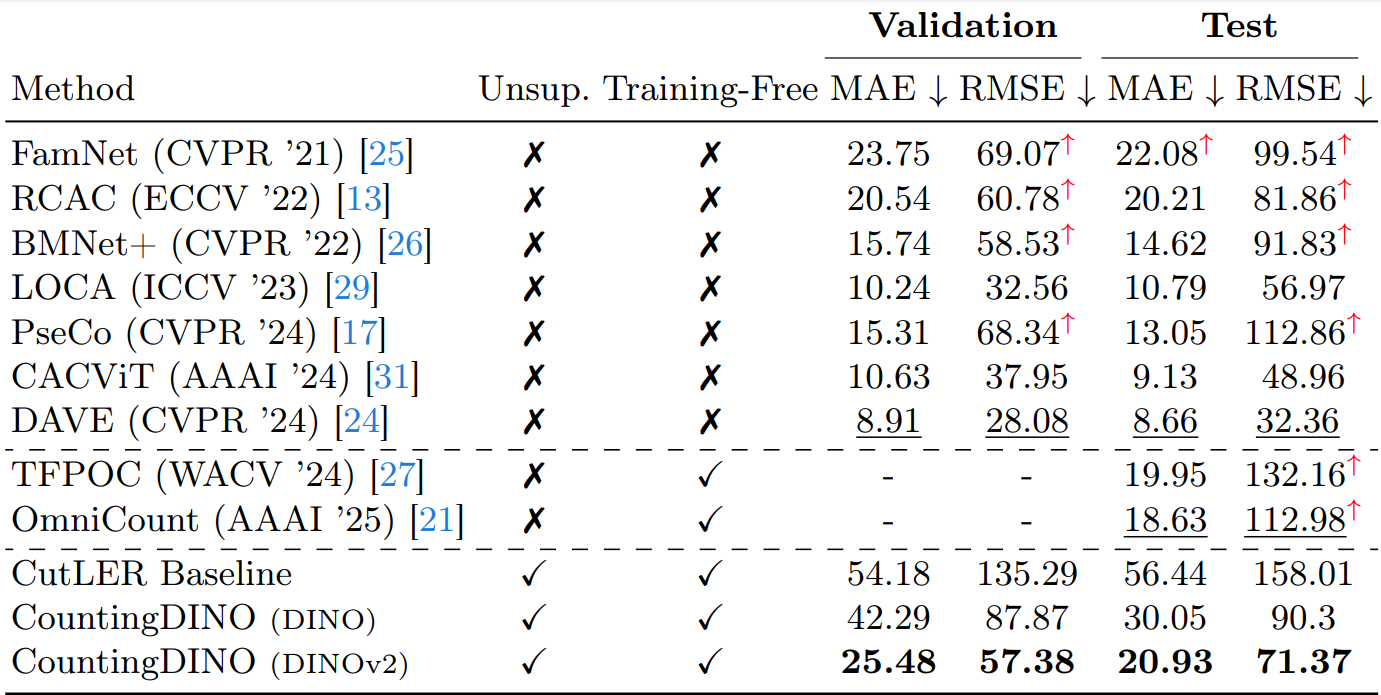
We evaluate our approach on the FSC-147 benchmark, where we outperform a baseline under the same label-free setting. Our method also achieves competitive — and in some cases superior — results compared to training-free approaches relying on supervised backbones, as well as several fully supervised state-of-the-art methods. This demonstrates that training-free CAC can be both scalable and competitive.
 This work has received financial support by the project FAIR – Future Artificial Intelligence Research - Spoke 1 (PNRR M4C2 Inv. 1.3 PE00000013) funded by the European Union - Next Generation EU.
This work has received financial support by the project FAIR – Future Artificial Intelligence Research - Spoke 1 (PNRR M4C2 Inv. 1.3 PE00000013) funded by the European Union - Next Generation EU.